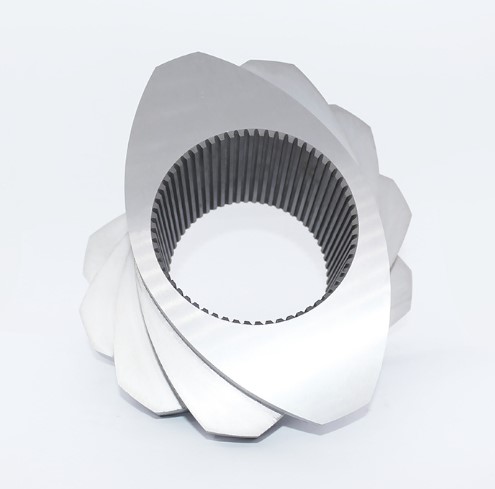
Shearing elements
Kneading blocks
Shearing element (kneading block)
Mechanism of action: By generating high shear force through staggered angles (30°, 45°, 60°, 90°), it achieves the dispersion and mixing (crushing of particles) and
distribution and mixing (component exchange) of materials.
Performance
The misalignment Angle ↑ → distributed mixing ↑, but the optimal dispersed mixing is achieved at 45°
Thickness ↑ → shear force ↑, but uniformity of mixing ↓
Application scenarios: Melting section pressurization, mixing section enhanced dispersion (such as glass fiber or carbon black filling)
Mixing element (TME)Grooves are made on the screw ribs (straight teeth/helical teeth), connecting adjacent screw grooves to facilitate longitudinal exchange
.
Advantages: High shear rate + low building pressure capacity, suitable for distributed mixing (such as color masterbatch dispersion or low-viscosity additive blending)
Material and durability
High-speed tool steel (W6Mo5Cr4V2) : Economical and universal;
Nitrided steel (38CrMoAlA) : Corrosion-resistant;
High-performance alloys: tungsten carbide (WC) alloy (with wear resistance increased by 7-8 times), Wr5 powder alloy (mainstream in Europe and America, with wear
resistance increased by 4-5 times),
suitable for highly abrasive fillers (such as glass fiber or minerals)
Process technology: Hot isostatic pressing (HIP) molding → Enhancing density and lifespan